Feature Spotlight: Audio Ducking
Soundscapes have the power to transport us to different worlds, evoke emotions, and tell compelling stories. Whether you're creating a guided tour, an immersive soundwalk, or any other location-based audio experience, clarity is paramount. That's where SonicMaps comes in with its latest feature: Audio Ducking.
What is Audio Ducking?
Audio ducking is a technique used in audio production to manage the balance between different audio tracks. It's all about prioritizing the most important sounds while reducing the volume of less important ones. Think of it as a dynamic volume control that automatically lowers the volume of background music or ambient sounds when a voice or dialogue track plays. This ensures that the voice remains clear and easily understood, even in the presence of other audio elements.
Why Audio Ducking Matters
- Clarity of Communication: In location-based audio experiences, such as guided tours or soundwalks, communication is key. Audio ducking ensures that the voice of the narrator or guide is never drowned out by background music or environmental sounds. Visitors can absorb the information seamlessly and enjoy a more engaging experience.
- Immersive Storytelling: Storytelling through sound relies on a delicate balance between different audio elements. With audio ducking, you can maintain the emotional impact of background music while ensuring that the narrative remains front and center. It enhances the immersive quality of your soundscapes.
- User Experience: Visitors using SonicMaps for self-guided tours or exploration can now enjoy an effortless experience. They no longer need to manually adjust volume settings on their devices to hear the narration clearly. Audio ducking does this automatically, making the experience user-friendly and hassle-free.
How to use Audio Ducking in SonicMaps
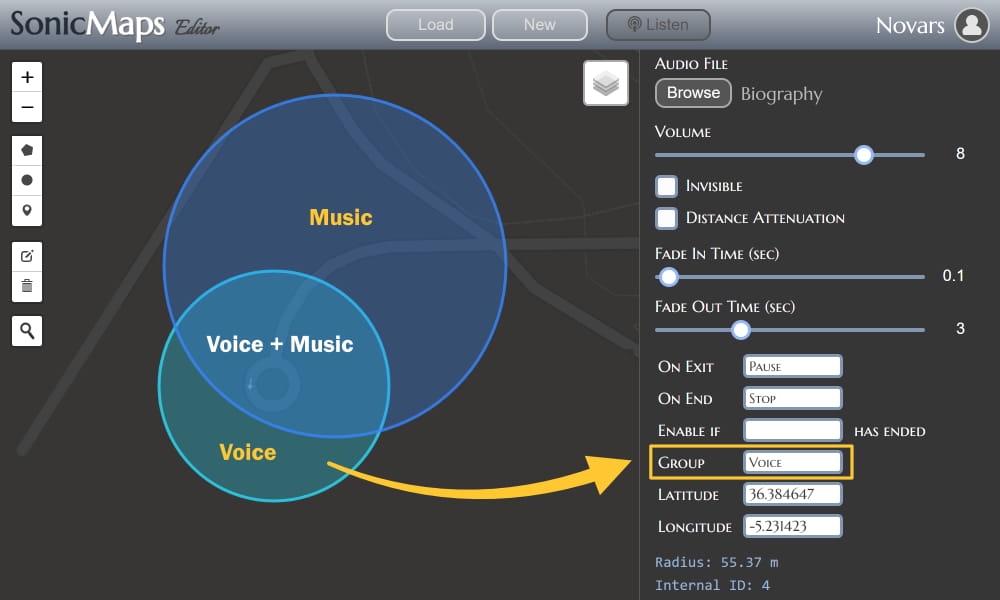
Enabling the Audio Ducking effect in the SonicMaps Editor is as simple as adding the zone containing your voice or dialogue to the "Voice" group. This tells SonicMaps that this particular audio track contains critical information and should take precedence over other audio elements. Therefore, when a user enters this zone, any other playing zone will be automatically attenuated.